People are excited to know about the complete information of different Land revenue systems in British India. Thus, Land Revenue Systems in British India: Zamindari, Ryotwari, and Mahalwari are one of the hot topics in UPSC Prelims and Mains. If you will go through the new syllabus then, “land reforms in India” is included in the GS Mains.
What were the Land revenue systems in ancient times?
If you need to know about the land revenue methodologies before British rule then go through the below points:
- In the earlier period, the prominent source of revenue for kings as well as emperors was “tax from the land.”
- For centuries, it is been noticed that there is a change in the ownership pattern of land.
- When there was a rule of Kingship, the complete land was divided into Jagirs. After this division, the Jagirs allot the land to Jagirdars. Finally, the Jagirdars divide the provided land and allocate it to their subordinate Zamindars.
Know more about Land Revenue Systems in British India: Zamindari, Ryotwari, and Mahalwari System
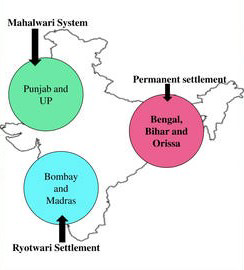
As we know, there are three prominent systems available related to land revenue collection in our country, “India.” These are named Zamindari, Ryotwari, and Mahalwari systems. Let us discuss it in brief.
Also Read: How to Focus on Study and Not Lose Your Time?
1. Zamindari System
- It is the permanent land revenue settlement that was introduced in the year 1793 by Cornwallis through the Permanent Settlement act.
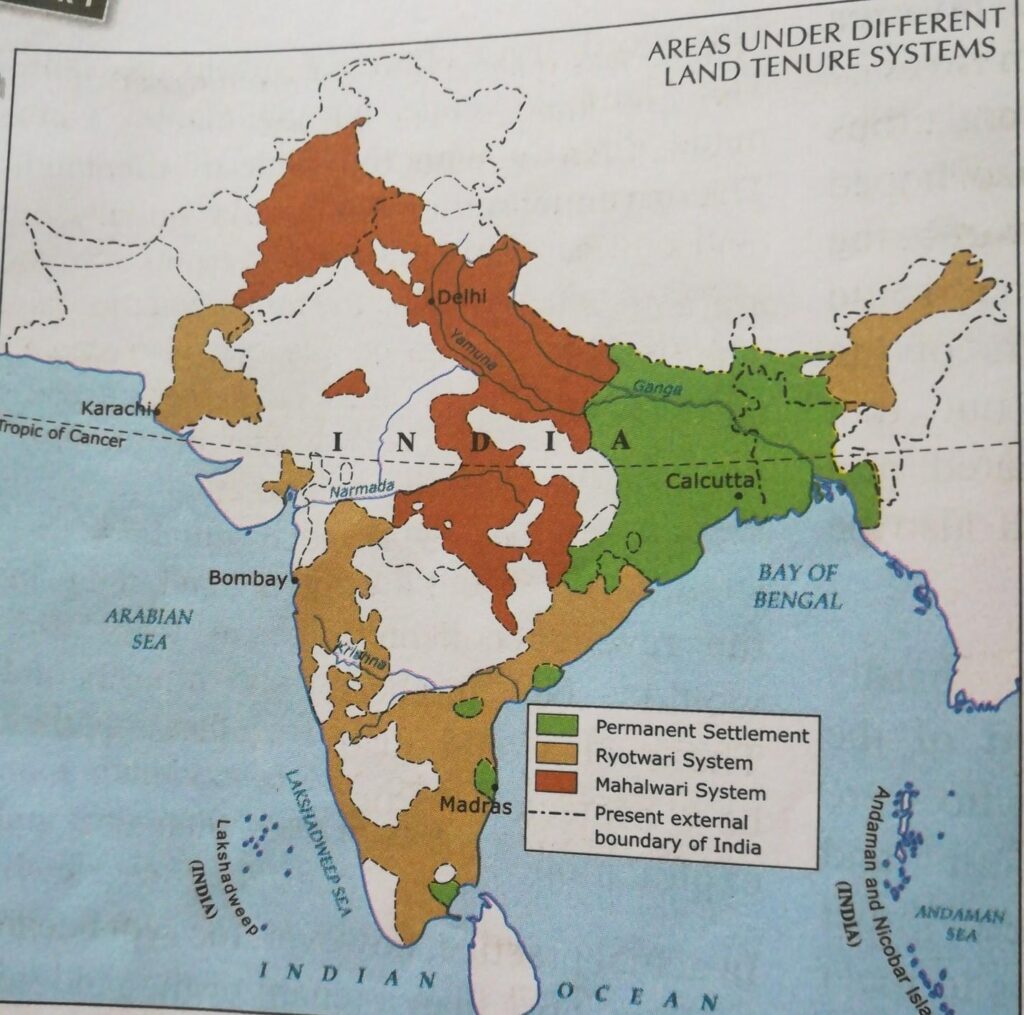
- This system was introduced under the rules and responsibilities of Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, and Varanasi.
- Zamindari system is also called as Permanent Settlement System.
- Under this system, it was declared that Zamindars are the owner of the lands. The Zamindars have the complete right to accumulate the rent from their farmers. Thus, the zamindars and farmers are called the owner and tenants respectively.
- The system asks the people to pay tax in cash even at the time of poor yield. When this system was not introduced, people are allowed to pay the tax in kind as well.
- The actual amount split into 11 parts. The division is done as 1/11 and 10/11 of the share for Zamindars and East India Company respectively.
2. Ryotwari System
- Another Land revenue system in British India which is the primary land revenue system in South India is the ryotwari system was introduced by a famous personality named Thomas Munro in the year 1820.
- The prominent areas which are included in this system are Madras, Bombay, a few parts of Assam, and the Coorg area of British India.
- In this system, the complete rights of ownership were accumulated by the peasants. Thus, the government used to collect the tax amount from the peasants directly.
- The revenue amount was divided as per the lands like 50% for the dry land and 60% for irrigated land.
- The tax amount under this system was increased frequently.
3. Mahalwari System
- In 1822, mahalwari system was introduced by Holt Mackenzie. While this system was upgraded in 1833 under the rules and power of William Bentick.
- Mahalwari settlement was declared as the primary land revenue system in Northwest India.
- The areas which are included under mahalwari settlement were Agra, Punjab, Gangetic Valley, Central Province, and North-West Frontier, etc of British India.
- The mahalwari system UPSC, the land was split into Mahals. Every mahal consists of one or more villages. Under this system, the complete amount of the land was accumulated from the farmers which were taken by the village headmen and not by the zamindar.
- The tax rates were hefty in mahalwari system upsc also.
- The system contains various provisions from other systems like Zamindari and Ryotwari.
Also Read: Top 6 Tips for Writing Biography
British Land Revenue System Policies created Various Problems
The major problem which was affected by the British Land revenue policies was, the “Agricultural Sector.”
How the problem was initiated?
The tax amount was not bearable by all the farmers. Thus, it was difficult to pay the complete amount before the deadline. In case, when the farmers were not able to pay the tax amount before the deadline. They try to take help from money lenders in a form of a loan amount which is provided with a high rate of interest. The farmers will be able to get loans after depositing their agricultural land. There can be circumstances when the farmers are not able to pay back the loan as well as interest. In such a situation, the money lenders have the complete right to seize their property.
Also Read: Read all Education News Here on Daily Basis.
Some other land reforms after Independence in India
The above points clearly illustrate the complete guide of Land Revenue Systems in British India: Zamindari, Ryotwari and Mahalwari systems. These are the various land revenue collection systems that are available in India.
After Independence in India, Zamindari Abolition Act was accepted by Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, UP, Bihar, etc. Zamindars have captured surplus lands. After some time, Land Ceilings Act was also acknowledged by various states.



